Elements are the core of every Hypar model. If you're not familiar with the idea of Elements, you can check out this introduction to Hypar's core concepts:
Hypar Core Concepts
How to create an element
In Grasshopper, you create elements with the "Construct Element" component:
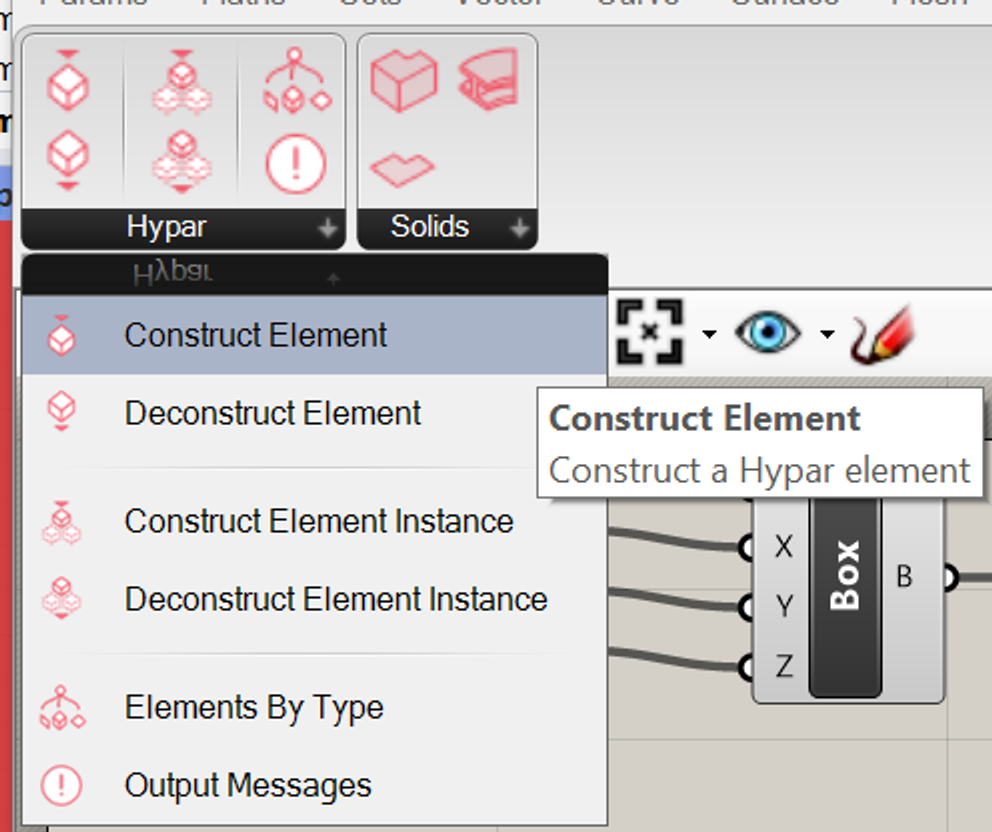
When you place an instance of it, it won't look like much. Right-click it to see the available element types you can create:
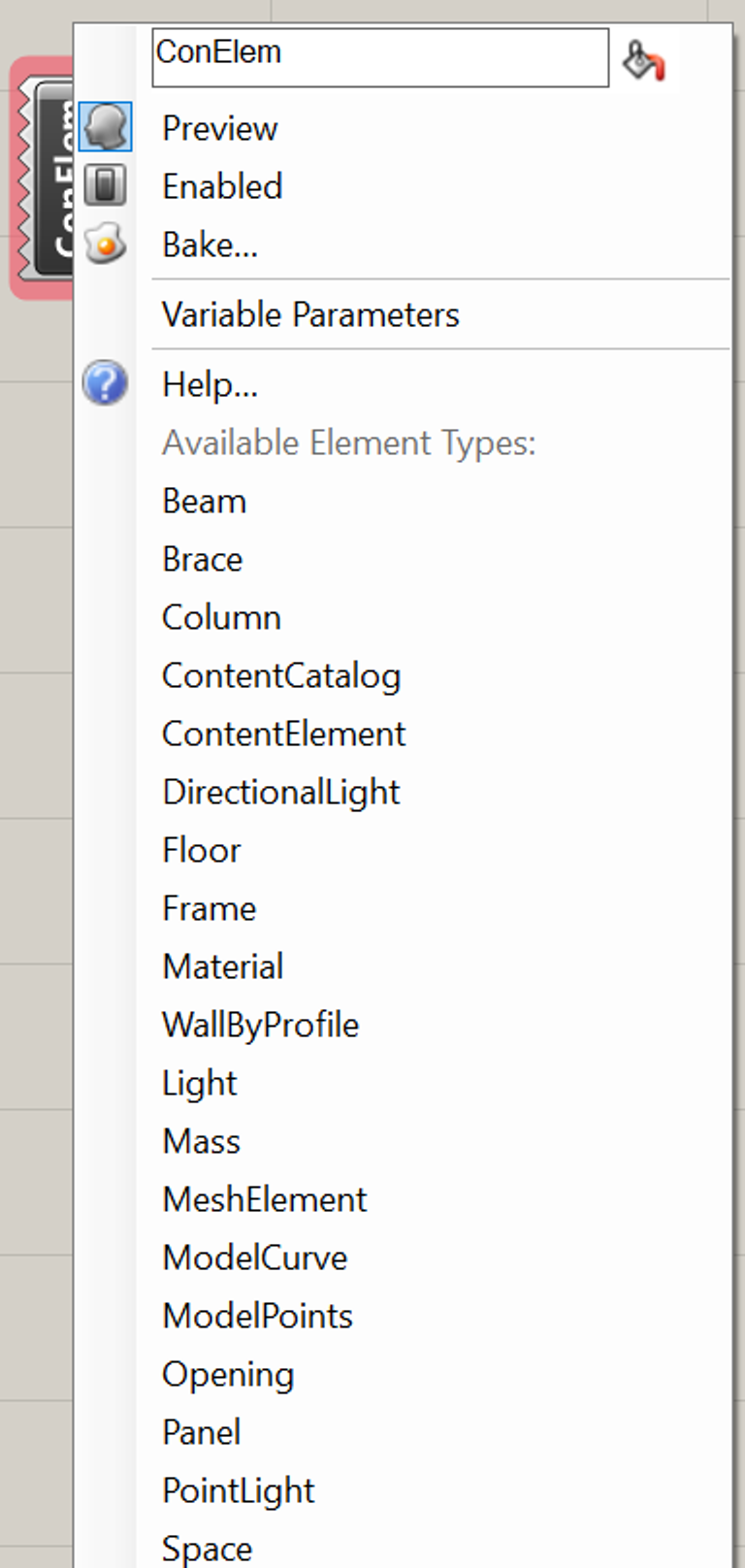
When you pick a type, inputs corresponding to that type will automatically be generated. For instance, if you select
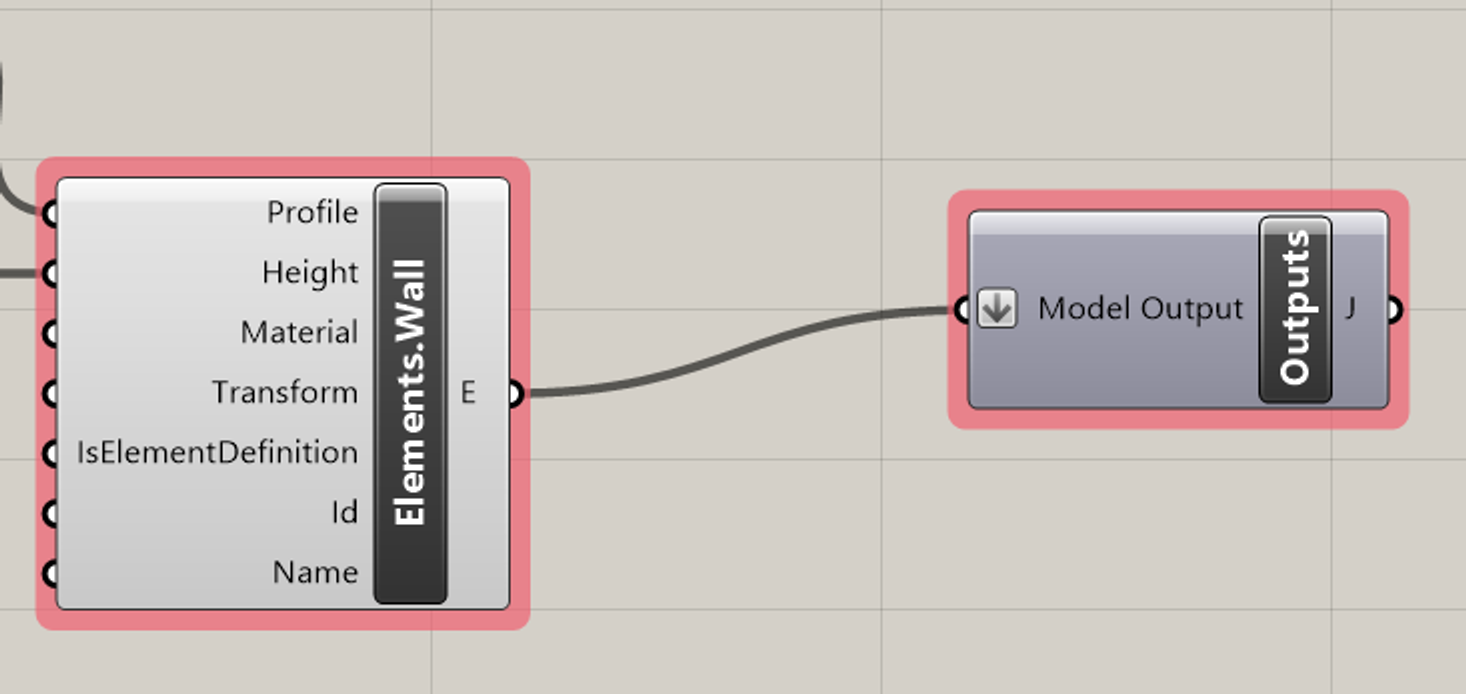
Wall the component will look like this: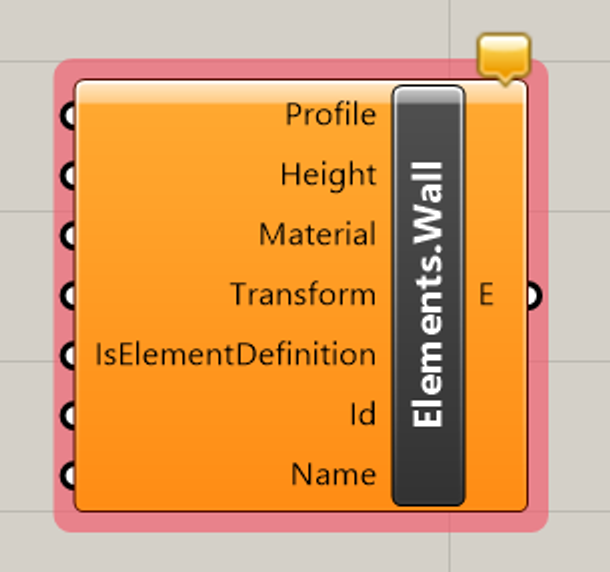
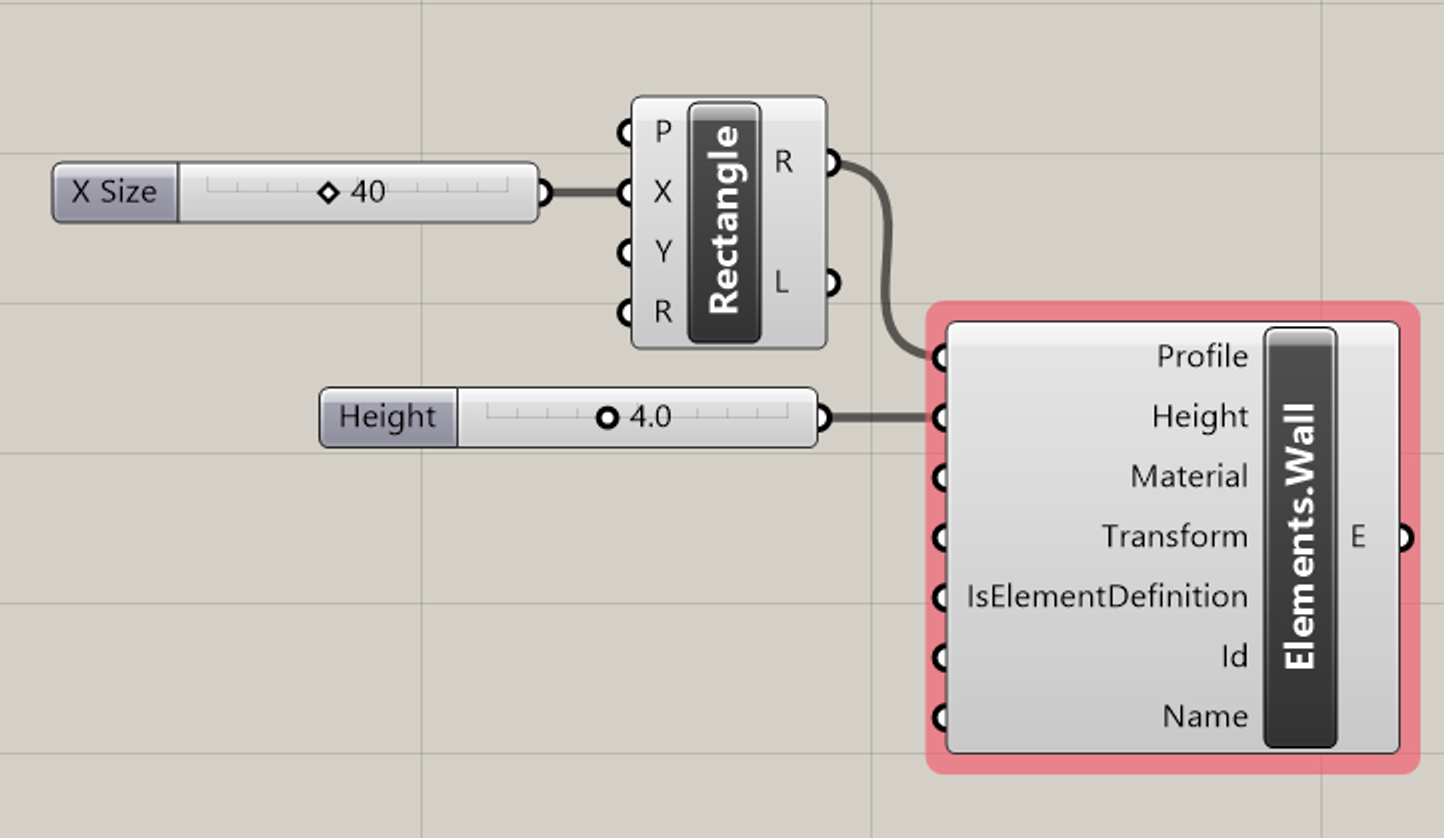
Note that a lot of the inputs are optional. Just supplying a profile and a height should be sufficient to create your wall:
To output this element to Hypar - so that you can see it, and other functions can depend on it, feed its output to your "Outputs" component. If you've given your function a model output name, look for that, otherwise it will just say "Model Output."
Elements work with data trees like any other Grasshopper component, so you can use one
Create Element component to create a number of elements at once.Remember to re-publish your function to see the changes on Hypar.
Working with other element types
In addition to the possible element types that come built-in, you can create other element types that you or others have defined. In the Hypar panel, choose "Edit Function Configuration"
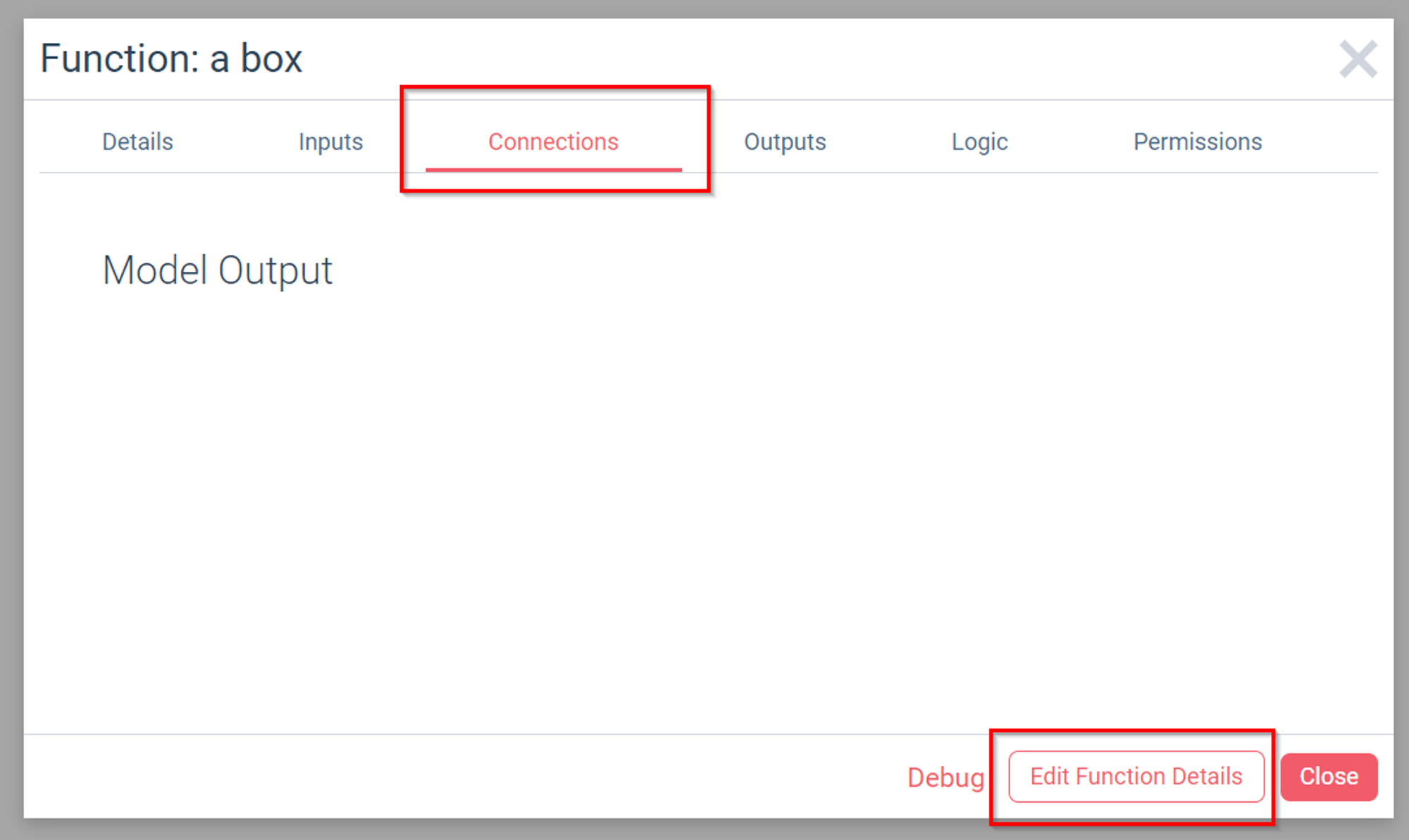
Once the window opens up and loads, go to the Connections tab and choose Edit Function Details.
Under Element Types, click + Add Row to add a new element type:
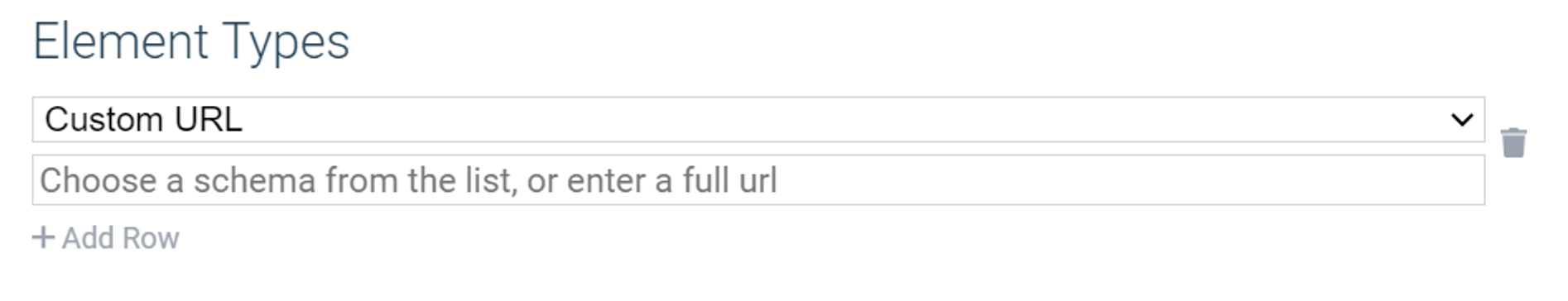
You can supply a URL to a custom element schema JSON, or just pick from among the available types. To learn more about custom element types, visit Element Types.
Once you're done adding element types, choose Save Changes, return to Grasshopper, and click OK.
The element types you've added should now be available in the right-click menu on
Construct Element.Representations
Some elements have a special property called
Representation, which is how a geometric expression is contributed to a custom element type. A Representation can be composed of one or more Solids, which can each be solid or void — this way it's possible to build up sophisticated geometries. In Grasshopper, it's fairly simple to construct a Representation: you can just supply a list of Solids from the Solid components:
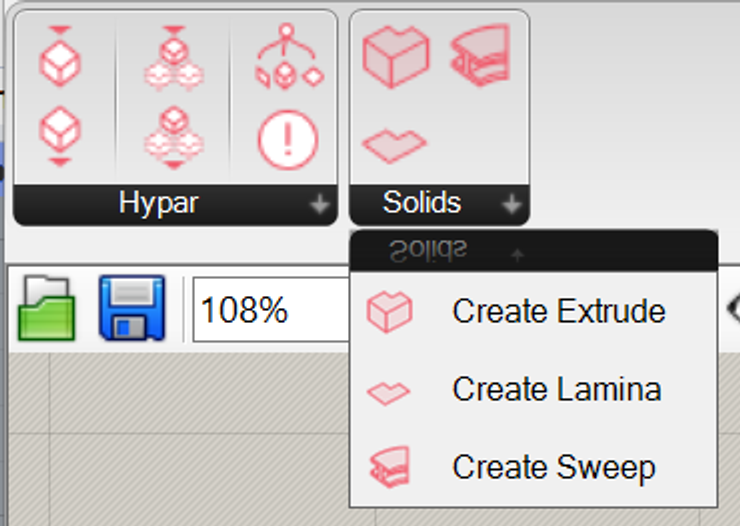
You can also create a Representation from any Brep with planar faces — it will convert automatically.
